21 DEVICES
21.8 Pointer (P)
219
21
21.8 Pointer (P)
Device used by instructions such as jump instruction (CJ instruction) and subroutine program call instruction (CALL
instruction, etc.). Types of pointers are as follows.
Pointers are used for the following purposes.
• Specifies label and where to jump to for jump instruction (CJ instruction).
• Specifies label (top of subroutine program) and call destination of subroutine instruction (CALL instruction, etc.).
Global pointers
Pointer for calling subroutine from all programs being run.
Precautions when using global pointers
• A global pointer of the same pointer number cannot be set as a label for more than one location.
• The initial pointer number for global pointers is fixed to "0".
Label assignment pointers
Pointer assigned to pointer type labels. Pointer for label assignment are automatically assigned to pointer type labels by
engineering tool. Pointer numbers of pointers for label assignment cannot be directly specified. By defining pointer type
labels, you can specify destination for jump instruction or subroutine program by label instead of pointer such as P0.
21.9 Interrupt Pointer (I)
Device used as label at top of interrupt program. Can be used by all running programs.
Setting the execution type of program to the event execution type eliminates the need to write (I) the
interrupt pointer. (Page 25 Generation of interrupt by interrupt pointer (I))
Pointer Description
Global pointers Pointers that can be referred to from all programs.
Label assignment pointers Pointers used by assignment to labels. Pointer numbers assigned to labels are automatically determined by engineering
tool; the user cannot specify pointer numbers to be assigned.
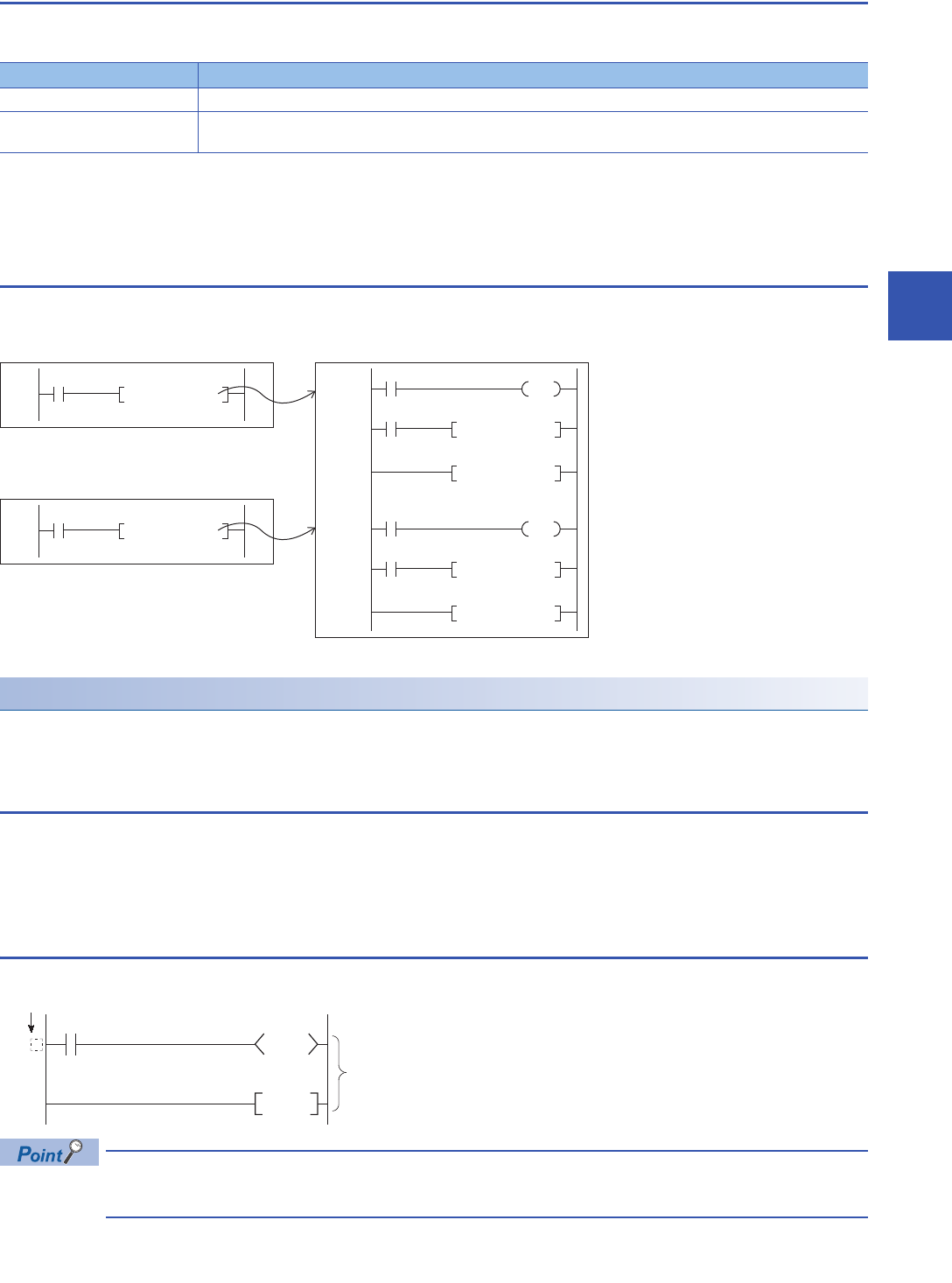
Program 2 (program group B)
CALL P1001
Program 1 (program group A)
RET
RET
CALL P1000
P1001
P1000
Program 3 (program group C)
Interrupt pointer (interrupt program label)
Interrupt Program
IRET
I


















