9 PID CONTROL FUNCTION
9.1 Outline of Function
55
9
9 PID CONTROL FUNCTION
9.1 Outline of Function
PID control is performed by PID control instruction. The PID instruction requires the system to calculate the output (MV) value
from the measured (PV) value. Through combining the P (proportional) action, I (integral) action, and D (derivative) action the
target (SV) value can be obtained.
• Alarm output function
The alarm function can be set for input variation (measured value) or output variation (value).
• Setting limit values
The upper limit and lower limit can be set for the output value.
• Auto-tuning function
The proportional gain (KP), integral time (TI) and differential time (TD) can be set automatically for both the limit cycle method
and step response method.
• Operation method of the PID instruction
Both PID speed type operation and measured value differential type operation are executed.
9.2 Basic Operation Expressions in PID Instruction
The PID instruction executes using the speed type or measured value differential type operation expression. According to the
contents of (s3)+1, bit 0 (operation setting (ACT)) specified by (s3) in the PID control, either forward operation or backward
operation is executed. Each value required in the operation is specified by a corresponding parameter (s3) or later.
Basic operation expression for PID control
Operation
setting (ACT)
(s3+1: b0)
Operation expression The meaning of the signs
Forward operation
(OFF)
EVn: Deviation in sampling at this time
EVn-1: Deviation in previous cycle
SV: Target value
PVnf: Measured value in sampling at this time
(after filter)
PVnf-1: Measured value in previous cycle
(after filter)
PVnf-2: Measured value in two cycles before
(after filter)
MV: Output variation
MVn: Operation quantity at this time
Dn: Differential term at this time
Dn-1: Differential term in previous cycle
TS: Sampling cycle
KP: Proportional gain
TI: Integral constant
TD: Differential constant
KD: Differential gain
Backward operation
(ON)
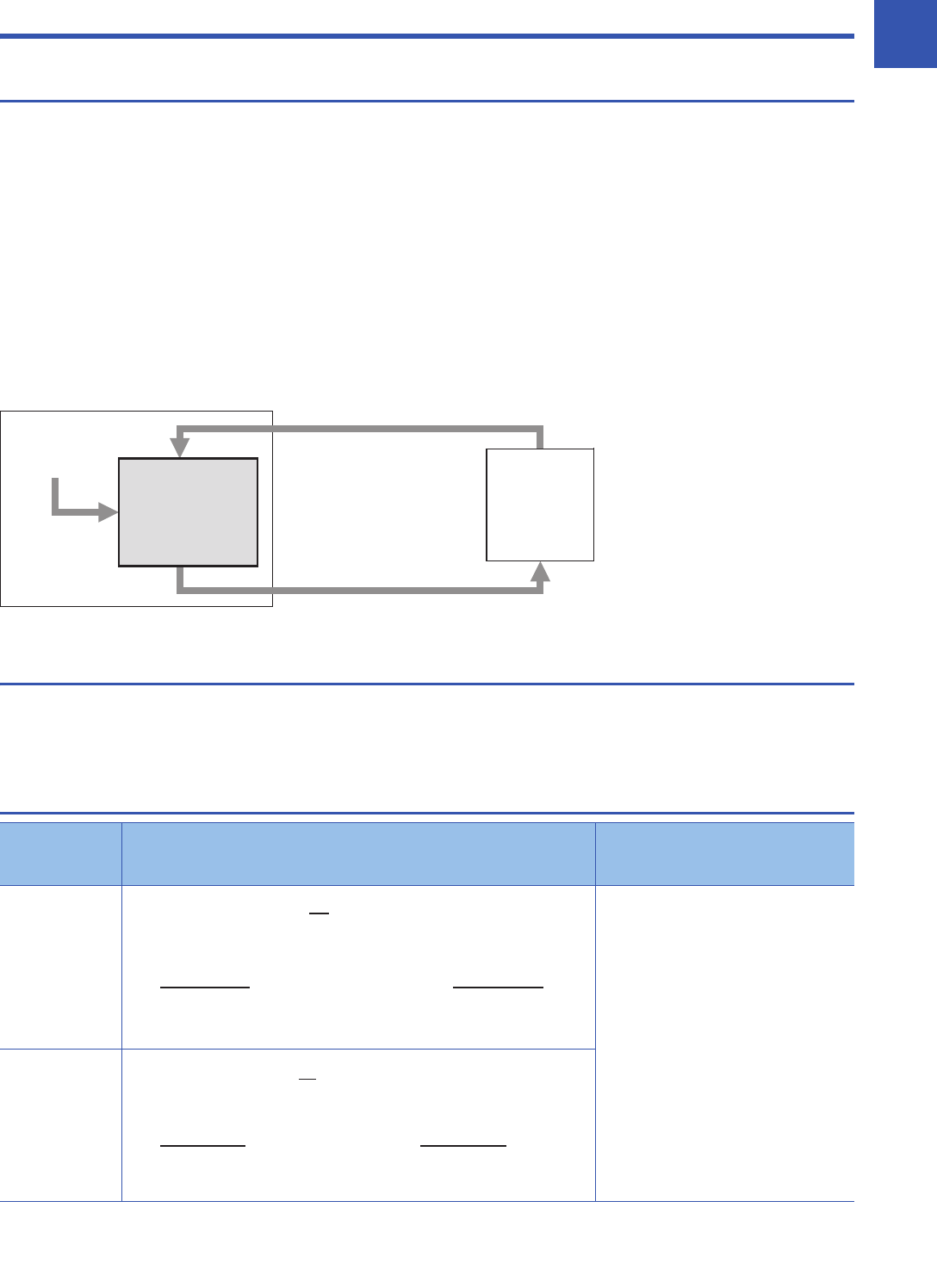
CPU module
Target value (SV)
Measured value (PV)
Controlled object
Output value (MV)
PID instruction
ΔMV=KP{(EVn-EVn-1)+
EVn=PVnf-SV
Dn=
MVn=ΣΔMV
TS
TI
TD
TS+KD•TD
KD•TD
TS+KD•TD
EVn+Dn}
(-2PVnf-1+PVnf+PVnf-2)+ •Dn-1
ΔMV=KP{(EVn-EVn-1)+
EVn=SV-PVnf
Dn=
MVn=ΣΔMV
TS
TI
TD
TS+KD•TD
KD•TD
TS+KD•TD
EVn+Dn}
(2PVnf-1-PVnf-PVnf-2)+
•Dn-1


















