Model T101 Instruction Manual Troubleshooting & Service
221
9.2.1. ZERO OR LOW SAMPLE FLOW
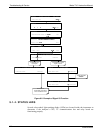
If the pump is operating but the unit reports a 0 gas flow, do the following three steps:
Check for actual sample flow
Check pressure
Carry out a leak check
To check the actual sample flow, disconnect the sample tube from the sample inlet on
the rear panel of the instrument. Make sure that the unit is in basic SAMPLE mode.
Place a finger over the inlet and see if it gets sucked in by the vacuum or, more properly,
use a flow meter to measure the actual flow. If there is proper flow of around 550-650
cm³/min, contact Technical Support. If there is no flow or low flow, continue with the
next step.
Check that the sample pressure is at or around 26 in-Hg-A (about 1” below ambient
atmospheric pressure).
9.2.2. HIGH FLOW
Flows that are significantly higher than the allowed operating range (typically ±10% of
the nominal flow) should not occur in the T101 unless a pressurized sample, zero or
span gas is supplied to the inlet ports. Be sure to vent excess pressure and flow just
before the analyzer inlet ports.
When supplying sample, zero or span gas at ambient pressure, a high flow would
indicate that one or more of the critical flow orifices are physically broken (very
unlikely case), allowing more than nominal flow, or were replaced with an orifice of
wrong specifications. If the flows are more than 15% higher than normal, we
recommend that the technician re-calibrate the flow electronically using the procedure in
Section 4.6.8, followed by a thorough and regular mo
nitoring of these flows to see if the
new setting is retained properly.
9.3. CALIBRATION PROBLEMS
This section presents som possible calibratio, problems and suggested solutions.
9.3.1. NEGATIVE CONCENTRATIONS
Negative concentration values can be caused for several things:
A slight, negative signal is normal when the analyzer is operating under
zero gas and the signal is drifting around the zero calibration point. This
is caused by the analyzer’s zero noise and may cause reported
concentrations to be negative for a few seconds at a time down to -20
ppb, but should alternate with similarly high, positive values.
Mis-calibration is the most likely explanation for negative concentration
values. If the zero air contained some H
2
S gas (contaminated zero air or
a worn-out zero air scrubber) and the analyzer was calibrated to that
concentration as “zero”, the analyzer may report negative values when
measuring air that contains little or no H
2
S. The same problem occurs, if
the analyzer was zero-calibrated using ambient air or span gas.
07266B DCN6485