Model T101 Instruction Manual Principles Of Operation
251
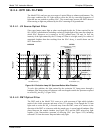
Another lens located between the excitation UV source lamp and the sample chamber
collimates the light emitted by the lamp into a steady, circular beam and focuses that
beam directly onto the reference detector. This allows the reference detector to
accurately measure the effective intensity of the excitation UV by:
Eliminating the effect of reflected light from the UV lamp reaching the PMT.
Making sure that all of the light emitted by the source lamp, passed though the 214 nm
filter and not absorbed by the SO
2
reaches the reference detector. Conversely, this also
makes sure that the volume of sample gas affected by the excitation beam is similar to
the volume of fluorescing SO
2
* being measured by the PMT, eliminating a possible
source of measurement offset.
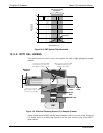
10.2.6. MEASUREMENT INTERFERENCES
It should be noted that the fluorescence method for detecting H
2
S is subject to
interference from a number of sources. The T101 has been successfully tested for its
ability to reject interference from most of these sources.
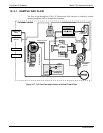
10.2.6.1. Direct Interference
Obviously, since the T101 measures H
2
S by converting it to SO
2
, the most significant
interfering gas for this measurement would be ambient SO
2
that is present in the sample
gas. The T101 circumvents this by passing the sample gas through a chemical scrubber
that removes all SO
2
from the sample gas before the H
2
S SO
2
conversion takes place.
This ensures that the only SO
2
present in the sample chamber is the result of the H
2
S
SO
2
conversion. Obviously to make sure that the analyzer operates correctly it is
important to make sure that this scrubber is functioning properly.
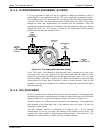
The second most common source of interference is from other gases that fluoresce in a
similar fashion to SO
2
when exposed to UV Light. The most significant of these is a
class of hydrocarbons called poly-nuclear aromatics (PNA) of which xylene and
naphthalene are two prominent examples. Nitric oxide fluoresces in a spectral range near
to SO
2
. For critical applications where high levels of NO are expected an optional
optical filter is available that improves the rejection of NO (contact Technical Support
for more information).
The Model T101 Analyzer has several methods for rejecting interference from these
gasses.
A special scrubber (kicker) mechanism removes any PNA chemicals present in the
sample gas before it the reaches the sample chamber.
The exact wavelength of light needed to excite a specific non-SO
2
fluorescing gas is
removed by the source UV optical filter.
The light given off by Nitrogen Oxide and many of the other fluorescing gases is outside
of the bandwidth passed by the PMT optical filter.
07266B DCN6485