102 UDC 3300 Process Controller Product Manual 4/00
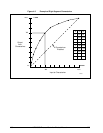
Figure 4-1 Example of Mass Flow Compensation using Multiplier/Divider Algorithm
Example - Mass Flow Compensation
A gas flow rate of 650 SCFM develops a differential pressure of 90" H O across an orifice plate
at reference conditions of 30 psig and 140 F. Compensate this gas flow for temperature and
pressure variations.
Apply Multiplier/Divider Algorithm:
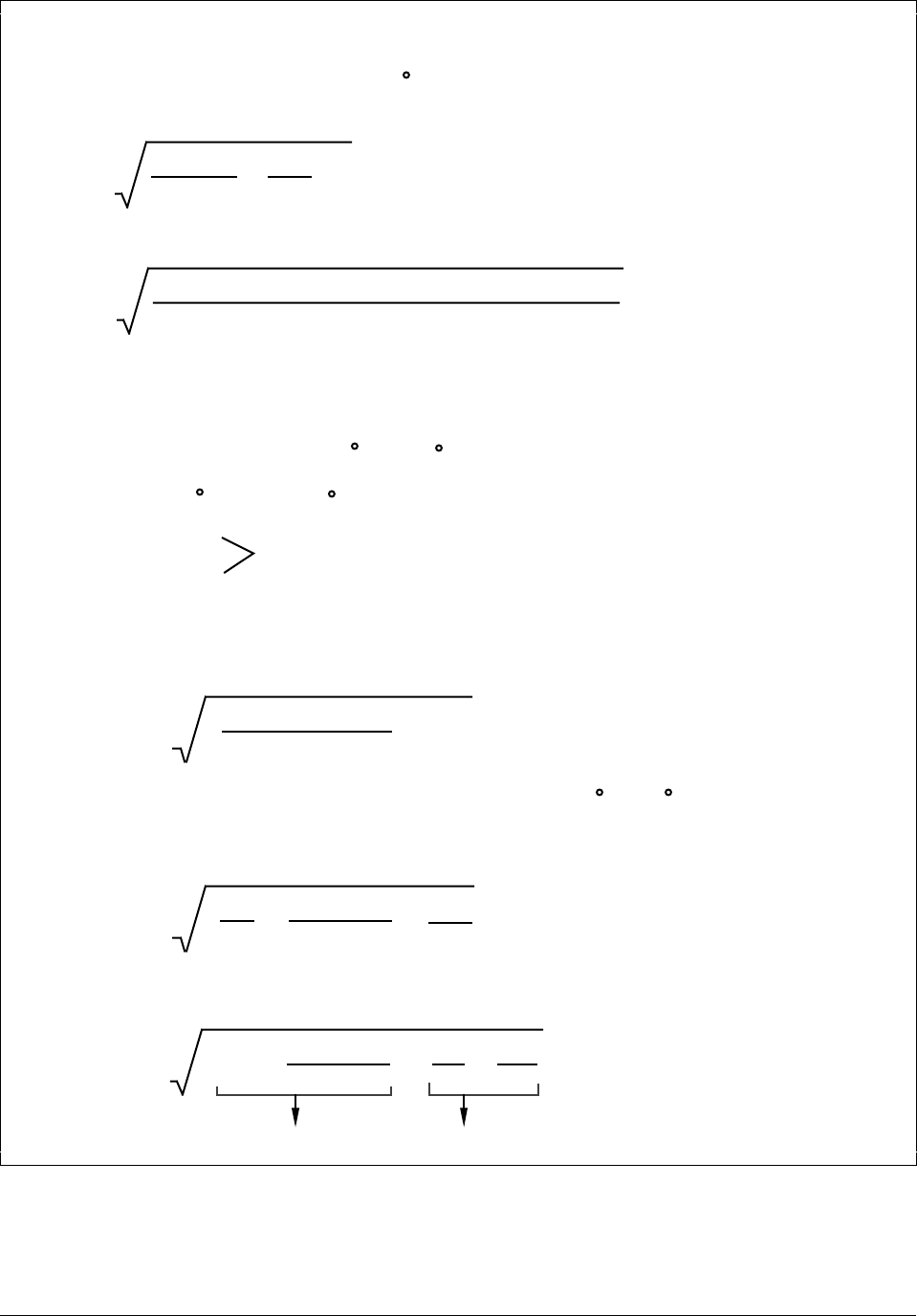
Flow = K
DP
f
xP
f
T
f
T
ref
x
P
ref
PV = K
(Input B x Ratio + Bias )BB
(Input A x Ratio + Bias ) x (Input C x Ratio + Bias )
A
AC
C
X (Calc – Calc )HI
LO
Where:
f = flowing conditions
ref = reference conditions (in absolute units)
Note: If temperature and pressure signals are already ranged in absolute units,
no Bias is required for inputs B and C.
Assign inputs using Engineering units:
Let:
Input A = DP = IN1 (in H O)
Input B = T = IN2 + Bias2 = IN2 F + 460 ( R)
Input C = P = IN3 + Bias3 = IN3psig + 14.7(psia)
T = 140 F + 460 = 600 R
P = 30 psig + 14.7 = 44.7 psia
Calc = 650.0
Calc = 0.0
2
f
f
ref
ref
Hi
Lo
Flow in SFCM at Reference Conditions
K = to be determined next
f
2
22049
Example continued
on next page
PV = Q =
DP
f
(IN3 + 14.7)x
SCFM
(IN2 + 460)
K
2
x
(650.0 - 0.0)
x
DP
f
90
(IN3 + 14.7)
x
(IN2 + 460)
T
ref
x
P
ref
SCFM
Q =
x
650
Note: When IN2 and IN3 are at the reference conditions of 600 R (140 F) and 44.7psia (30
psig) respectively and DP = 90" H O, the equation must calculate 650 SCFM. To accomplish
this, divide the DP value by "90" to normalize the equation.
2
f
Rearranging terms:
Variable
Constant = K
2
DP
f
(IN3 + 14.7)
x
(IN2 + 460)
x
1
90
T
ref
P
ref
xx
650
SCFM
Q =