Teledyne API - Model 200EH/EM Operation Manual Troubleshooting & Repair
231
11. TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR
This section contains a variety of methods for identifying and solving performance problems with the analyzer.
NOTE
The operations outlined in this chapter must be performed by qualified
maintenance personnel only.
CAUTION
Risk of electrical shock. Some operations need to be carried out with
the analyzer open and running. Exercise caution to avoid electrical
shocks and electrostatic or mechanical damage to the analyzer. Do not
drop tools into the analyzer or leave those after your procedures. Do
not shorten or touch electric connections with metallic tools while
operating inside the analyzer. Use common sense when operating
inside a running analyzer.
11.1. GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING
The analyzer has been designed so that problems can be rapidly detected, evaluated and repaired. During
operation, the analyzer continuously performs diagnostic tests and provides the ability to evaluate its key
operating parameters without disturbing monitoring operations.
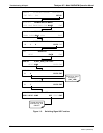
A systematic approach to troubleshooting will generally consist of the following five steps:
Note any warning messages and take corrective action as necessary.
Examine the values of all TEST functions and compare them to factory values. Note any major
deviations from the factory values and take corrective action.
Use the internal electronic status LED’s to determine whether the electronic communication channels
are operating properly. Verify that the DC power supplies are operating properly by checking the
voltage test points on the relay board. Note that the analyzer’s DC power wiring is color-coded and
these colors match the color of the corresponding test points on the relay board.
Suspect a leak first! Customer service data indicate that the majority of all problems are eventually
traced to leaks in the pneumatic system of the analyzer (including the external pump), the source of zero
air or span gases or the sample gas delivery system. Check for gas flow problems such as clogged or
blocked internal/external gas lines, damaged seals, punctured gas lines, a damaged pump diaphragm,
etc.
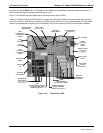
Follow the procedures defined in Section 3.2.4. to confirm that the analyzer’
s vital functions are working
(pow
er supplies, CPU, relay board, keyboard, PMT cooler, etc.). See Figure 3-1, Figure 3-2, and Figure
3-3 for general layout of components and sub-as
semblies in the analyzer. See the wiring interconnect
diagram (document 04504) and interconnect list (document 04496) in Appendix D.
04521C (DCN5731)