Teledyne API - Model 200EH/EM Operation Manual Operating Instructions
65
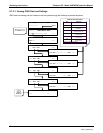
6.7.1.2. iDAS Parameters
Data parameters are types of data that may be measured by the analyzers instrumentality concentrations of
measured gases, temperatures of heated zones,, pressures and flows of the pneumatic subsystem as well as
calibration data such as slope and offset for each gas. For each Teledyne Instruments analyzer model, the list
of available data parameters is different, fully defined and not customizable (see Appendix A.5 for a list of
M200EH/EM parameters).
Most data parameters have associated measurement units, such as mV, ppm, cm³/min, etc., although some
parameters have no units. The only units that can be changed are those of the concentration readings
according to the
SETUP-RANGE settings.
NOTE
The iDAS does not keep track of the unit of each concentration value and iDAS data files
may contain concentrations in multiple units if the unit was changed during data
acquisition.
Each data parameter has user-configurable functions that define how the data are recorded.
Table 6-8: iDAS Data Parameter Functions
FUNCTION EFFECT
PARAMETER
Instrument-specific parameter name.
SAMPLE MODE INST: Records instantaneous reading.
AVG: Records average reading during reporting interval.
MIN: Records minimum (instantaneous) reading during reporting interval.
MAX: Records maximum (instantaneous) reading during reporting interval.
SDEV:
Records the standard deviation of the data points recorded during the reporting
interval.
PRECISION
Decimal precision of parameter value(0-4).
STORE NUM.
SAMPLES
OFF: stores only the average (default).
ON: stores the average and the number of samples in each average for a parameter.
This property is only useful when the AVG sample mode is used. Note that the
number of samples is the same for all parameters in one channel and needs to be
specified only for one of the parameters.
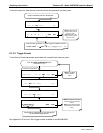
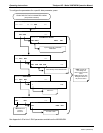
6.7.1.3. iDAS Triggering Events
Triggering events define when and how the iDAS records a measurement of any given data channel. Triggering
events are firmware-specific and are listed in Appendix A-5. The most common triggering events are:
ATIMER: Sampling occurs at regular intervals specified by an automatic timer. Trending information is
often stored via such intervals, as either individual datum or averaged.
EXITZR, EXITSP, SLPCHG (exit zero, exit span, slope change): Sampling at the end of an irregularly
occurring event such as calibration or when the slope changes. These events create individual data
points. Zero and slope values can be used to monitor response drift and to document when the
instrument was calibrated.
WARNINGS: Some data may be useful when stored if one of several warning messages appears. This
is helpful for trouble-shooting by monitoring when a particular warning occurred.
04521C (DCN5731)