Teledyne API - Model 200EH/EM Operation Manual Troubleshooting & Repair
259
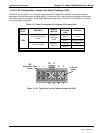
11.5.9. MOTHERBOARD
11.5.9.1. A/D functions
A basic check of the analog to digital (A/D) converter operation on the motherboard is to use the Signal I/O
function under the DIAG menu. Check the following two A/D reference voltages and input signals that can be
easily measured with a voltmeter.
Using the
Signal I/O function (Section 6.13.1 Appendix D), view the value of REF_4096_MV and
REF_GND. If both are within 3 mV of their nominal values (4096 and 0) and are stable to within ±0.5
mV, the basic A/D converter is functioning properly. If these values fluctuate largely or are off by more
than 3 mV, one or more of the analog circuits may be overloaded or the motherboard may be faulty.
Choose one parameter in the Signal I/O function such as
SAMPLE_PRESSURE (see previous section
on how to measure it). Compare its actual voltage with the voltage displayed through the
SIGNAL I/O
function. If the wiring is intact but there is a difference of more than ±10 mV between the measured and
displayed voltage, the motherboard may be faulty.
11.5.9.2. Analog Output Voltages
To verify that the analog outputs are working properly, connect a voltmeter to the output in question and perform
an analog output step test as described in Section 6.13.3.
For each of the steps, taking into account any offset
that may have been programmed into the channel (Section
6.13.4.4), the output should be within 1% of the nominal value listed in the table below except for the 0% step,
which should be within 2-3 mV. If one or more of the steps is outside of this range, a failure of one or both D/A
converters and their associated circuitry on the motherboard is likely.
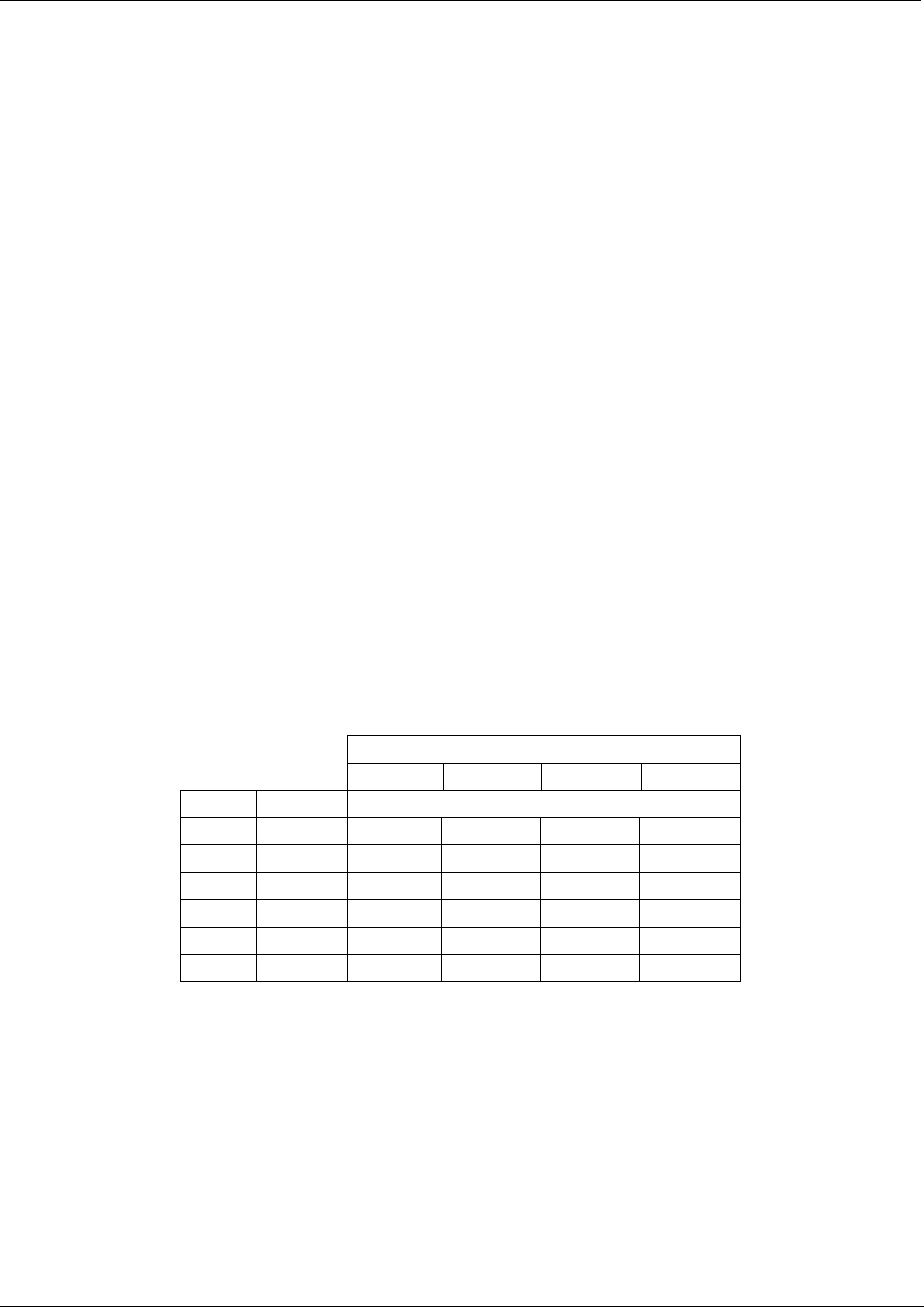
Table 11-9: Analog Output Test Function - Nominal Values
FULL SCALE OUTPUT VOLTAGE
100mV 1V 5V 10V
STEP % NOMINAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
1 0 0 mV 0 0 0
2 20 20 mV 0.2 1 2
3 40 40 mV 0.4 2 4
4 60 60 mV 0.6 3 6
5 80 80 mV 0.8 4 8
6 100 100 mV 1.0 5 10
04521C (DCN5731)