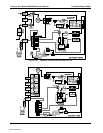
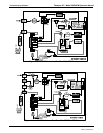
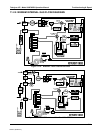
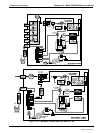
Teledyne API - Model 200EH/EM Operation Manual Troubleshooting & Repair
245
The most likely cause for zero or low ozone flow is a clogged critical flow orifice or sintered filter within
the orifice assembly. The orifice that sets the ozone flow is located on the reaction cell. Check the
actual ozone flow by disconnecting the tube from the reaction cell and measuring the flow going into the
cell. If this flow is correct (see Table 10-3 for flow rates), the orifice works properly. If this flow is low,
replace or clean the orifice. The orifice holder assembly allows a quick and easy replacement of the
orifice, refer to Section 9.3.8 on how to do this. Appendix B lists a spare p
art kit with a complete orifice
a
ssembly that allows a quick replacement with minimum instrument down-time. The clogged orifice can
then be cleaned while the instrument is running with the replacement.
11.2.4. HIGH FLOW
Flows that are significantly higher than the allowed operating range (typically ±10-11% of the nominal flow)
should not occur in the M200EH/EM unless a pressurized sample, zero or span gas is supplied to the inlet ports.
Ensure to vent excess pressure and flow just before the analyzer inlet ports.
When supplying sample, zero or span gas at ambient pressure, a high flow would indicate that one or more of
the critical flow orifices are physically broken (very unlikely case), allowing more than nominal flow, or were
replaced with an orifice of wrong specifications. If the flows are within 15% higher than normal, we recommend
to re-calibrate the flow electronically using the procedure in Section 6.13.7.5, followed by a regular review of
these flo
ws over time to see if the new setting is retained prope
rly.
11.2.5. SAMPLE FLOW IS ZERO OR LOW BUT ANALYZER REPORTS
CORRECT FLOW
Note that the M200EH/EM analyzer can report a correct flow rate even if there is no or a low actual sample flow
through the reaction cell. The sample flow on the M200EH/EM is only calculated from the sample pressure and
critical flow condition is verified from the difference between sample pressure and vacuum pressure. If the
critical flow orifice is partially or completely clogged, both the sample and vacuum pressures are still within their
nominal ranges (the pump keeps pumping, the sample port is open to the atmosphere), but there is no flow
possible through the reaction cell.
Although measuring the actual flow is the best method, in most cases, this fault can also be diagnosed by
evaluating the two pressure values. Since there is no longer any flow, the sample pressure should be equal to
ambient pressure, which is about 1 in-Hg-A higher than the sample pressure under normal operation. The
reaction cell pressure, on the other hand, is significantly lower than under normal operation, because the pump
no longer has to remove 500 cm³/min of sample gas and evacuates the reaction cell much better. Those two
indicators, taken together with a zero or low actual flow, indicate a clogged sample orifice.
The M200EH/EM features a new orifice holder, which makes switching sample and ozone flow orifices very
easy, refer to Section 9.3.8 on how to change the sample orifices a
nd Appendix B for part numbers of these
assemblies. Again, monitoring the pr
essures and flows regularly will reveal such problems, because the
pressures would slowly or suddenly change from their nominal, mean values. Teledyne Instruments
recommends to review all test data once per week and to do an exhaustive data analysis for test and
concentration values once per month, paying particular attention to sudden or gradual changes in all parameters
that are supposed to remain constant, such as the flow rates.
04521C (DCN5731)