178
CHAPTER 8 OPR CONTROL
This chapter describes OPR control.
8.1 Overview of OPR Control
In "OPR control", a starting point (or OP) of major positioning control is set, and positioning is executed toward the
original point. Use this control to return a machine system at a position other than its OP to the OP when the QD73A1
turned on OPR request signal (X12) at power-on, or after a positioning stop.
OPR request signal (X12) turns on at the following timings.
• When the power is turned on
• When the CPU module was reset
• When OPR starts
• When Servo READY signal (READY) turns off while BUSY signal (X14) is on
• When Servo READY signal (READY) turns off while BUSY signal (X14) is off
(only when "0: Clear the deviation counter when the servo ready signal is OFF." is selected for "Deviation
counter clear setting" in the switch setting)
(1) OPR method
The QD73A1 has two OPR methods so that an OP can be established in the optimum method (determination of
the OP position, or OPR completion) depending on the positioning system configuration or the application.
Set an OPR method in the switch setting. For the setting method, refer to the following.
Page 100, Section 6.2
*1 Signal that is output as a single pulse at one motor revolution (e.g. Z-phase signal output from the drive unit)
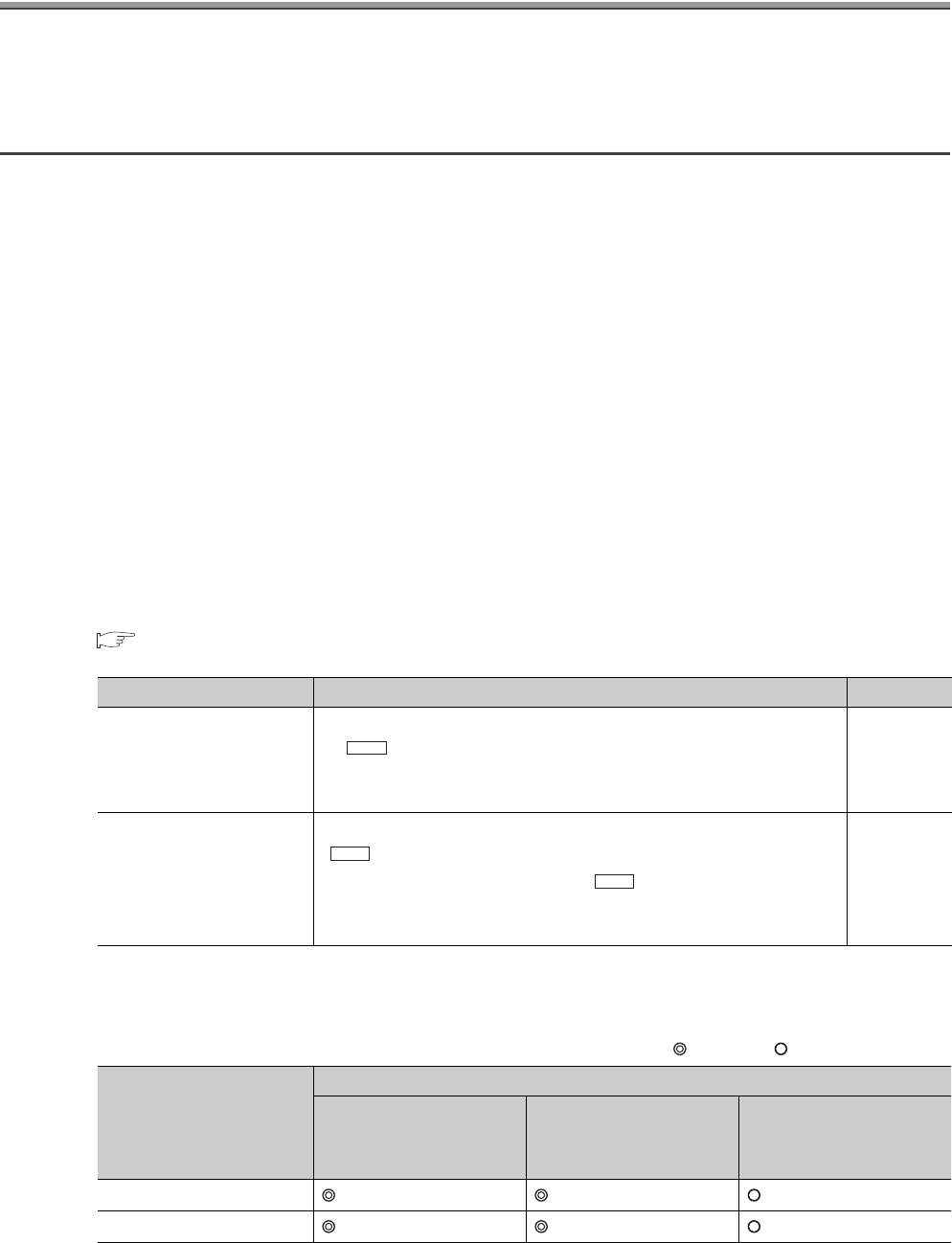
(2) External I/O signals used for OPR control
: Necessary : Necessary as required
OPR method Operation detail Reference
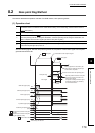
Near-point dog method
As the near-point dog turns on, deceleration starts. (The speed decelerates
to " Creep speed".) After the near-point dog turned off, the OPR is
completed at the operation stop with the first Zero signal
*1
, specifying the
position as the OP.
Page 179,
Section 8.2
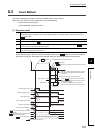
Count method
As the near-point dog turns on, deceleration starts and the machine moves at
" Creep speed". From the position where the near-point dog turned on,
the machine moves the distance set in " Setting for the movement
amount after near-point dog ON". Then, the OPR is completed at the
operation stop with the first Zero signal
*1
.
Page 181,
Section 8.3
OPR method
Signal required for control
Near-point dog signal
(DOG)
Zero signal
Upper limit signal
(FLS)/Lower limit signal
(RLS)
Near-point dog method
Count method
Pr.12
Pr.12
Pr.13