1 - 4
MELSEC-
A
1 PRODUCT OUTLINE
1.1.2 Purpose and applications of positioning control
"Positioning" refers to moving a moving body, such as a workpiece or tool (hereinafter,
generically called "workpiece") at a designated speed, and accurately stopping it at the
target position. The main application examples are shown below.
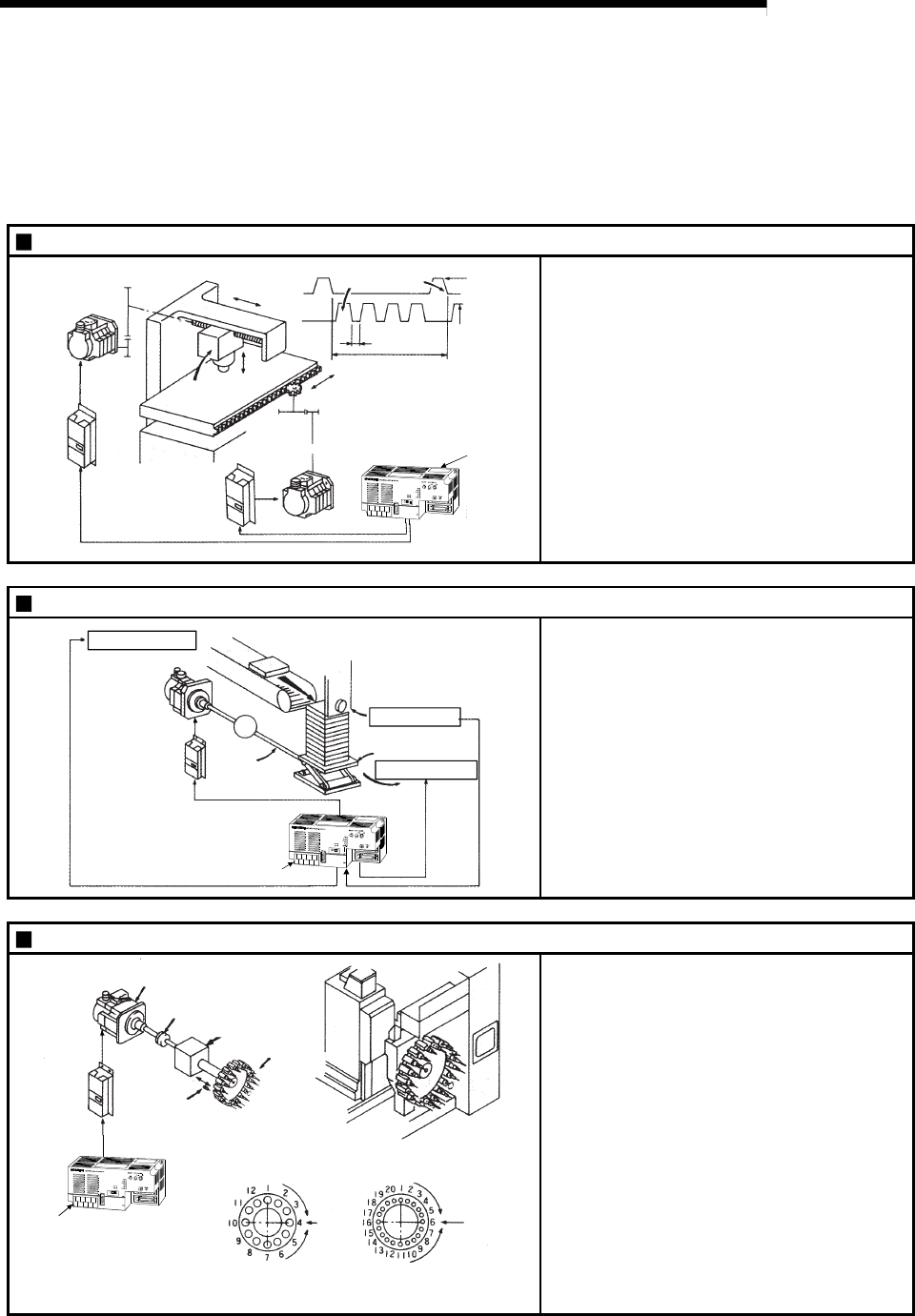
Punch press (X, Y feed positioning)
Y axis
servomotor
Gear and ball screw
Y axis
X axis
Y axis
320mm
160mm
15m/min
(2000r/min)
15m/min
(1875r/min)
12 s
Press head
Servo
a
mplifier
X axis
Gear and rack & pinion
X axis
servomotor
X axis
Y axis
Servo
amplifier
Press
punching
D75P2
To punch insulation material or leather, etc.,
as the same shape at a high yield, positioning
is carried out with the X axis and Y axis
servos.
After positioning the table with the X axis
servo, the press head is positioned with the Y
axis servo, and is then punched with the
press.
When the material type or shape changes, the
press head die is changed, and the positioning
pattern is changed.
Palletizer
Servo amplifier
Conveyor control
Conveyor
Servomotor
(with brakes)
Position detector
Reduction
gears
Ball screw
(From D75P2)
Palletizer
Unloader control
G
D75P2
Using the servo for one axis, the palletizer is
positioned at a high accuracy.
The amount to lower the palletizer according to
the material thickness is saved.
Compact machining center (ATC magazine positioning)
Servomotor
Servo
amplifier
Coupling
ATC tool
magazine
Reduction
gears
Positioning
pin
Tool
(12 pcs., 20 pcs.)
<No. of tools: 12> <No. of tools: 20>
Current
value
retrieval
position
Current
value
retrieval
position
Rotation direction
for calling
11, 12, 1, 2 or 3
Rotation direction
for calling
17 to 20, 1 to 5
Rotation direction
for calling 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 or 10
Rotation direction
for calling 7 to 16
D75P2
The ATC tool magazine for a compact
machining center is positioned.
The relation of the magazine's current value
and target value is calculated, and positioning
is carried out with forward run or reverse run to
achieve the shortest access time.