Appendix - 28
MELSEC-
A
APPENDICES
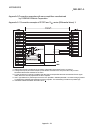
ABSOLUTE ENCODER
This is a detector that enables the angle data
within 1 motor rotation to be output to an
external destination. Absolute encoders are
generally able to output 360
°
in 8 to 12 bits.
Incremental encoders have a disadvantage in
that the axis position is lost when a power
failure occurs. However, with absolute
encoders, the axis position is not lost even
when a power failure occurs.
Various codes such as a binary code and BCD
code can be output.
Absolute encoders are more expensive, more
accurate, and larger than incremental
encoders. Refer to "ENCODER".
2
2
2
2
0
1
3
4
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
Slit disk
Phototransistor
Fixed slit
Light-emitting diode
Rotating
axis
Binary code
ABSOLUTE POSITION DETECTION
SYSTEM
When positioning is carried out using this
system, a zero point return can be carried out
once when the device is started to allow the
machine position to be stored in the memory
and the current position to be held even when
the power is turned OFF. These will be
compensated if mechanical deviation occurs,
so a zero point return is not required after the
power is turned ON again. A motor with an
absolute position detector and servo amplifier
and positioning module compatible with an
absolute position detection system are
required to configure this system.
ABSOLUTE SYSTEM
This is one system for expressing a positioning
address.
Absolute address system.
This system uses 0 as a reference, and
expresses the address as the distance from 0.
The direction is automatically determined,
even when it is not designated. The other
address system is the increment system.
No.10 No.2 No.3
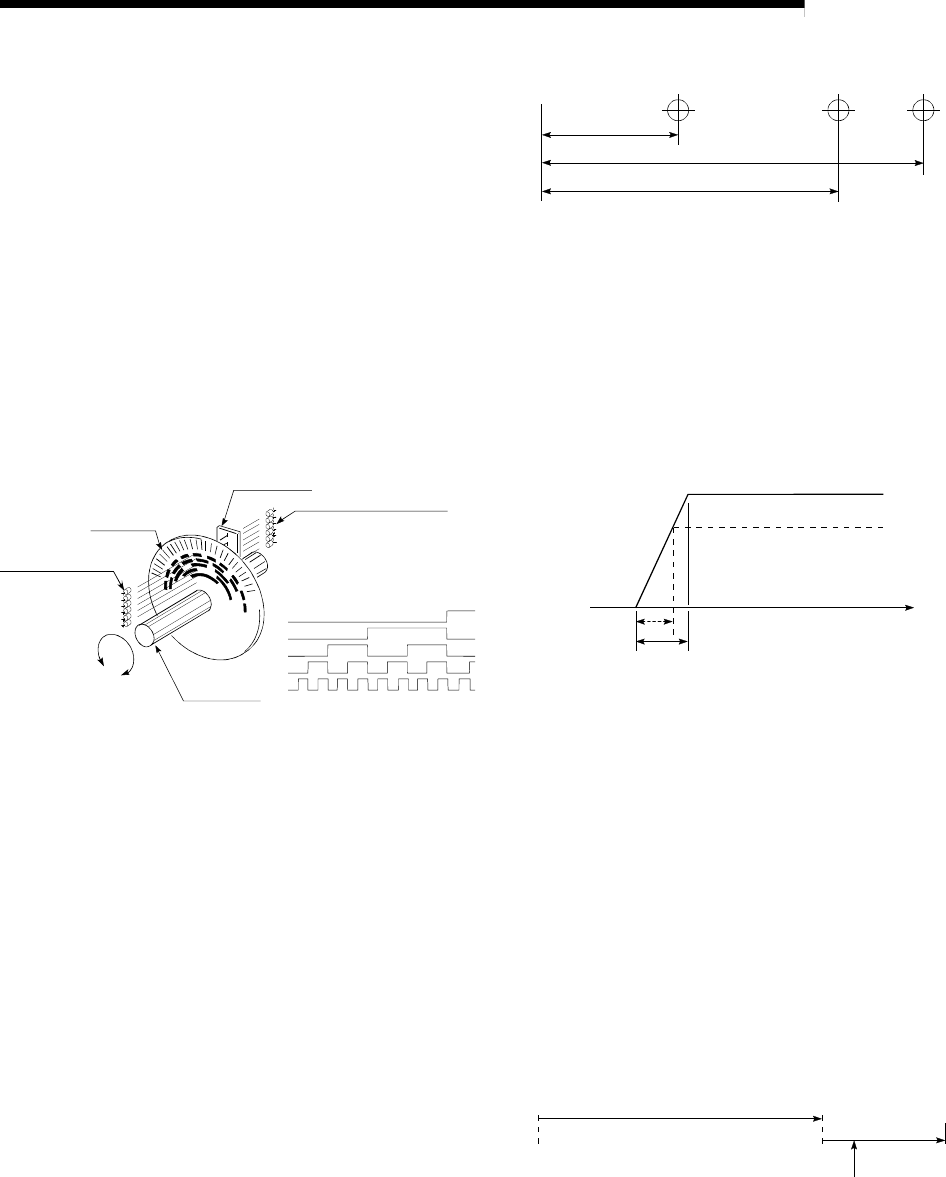
ACCELERATION TIME
The parameter acceleration time refers to the
time from a stopped state to the time the
speed limit value is reached, so it becomes
proportionally shorter as the setting speed
decreases. The acceleration time is
determined by factors such as machine inertia,
motor torque, and load resistance torque.
Speed limit value
Setting speed
Speed 0
Acceleration time
Time
ADDRESS
1) This is a numerical value to express the
positioning position, designated in mm, inch,
angle, or No. of pulse units.
2) The memory address. Many addresses are
stored in the memory. An address is read or
written after it is designated.
AFTER mode
This is the mode that outputs the M code after
positioning is complete (after stopping).
Clamping can be commanded, drilling
dimensions can be selected, etc., with this
mode.
OFFON
No.11No.10
Positioning
M code (8)
Clam
p
command