Appendix - 35
MELSEC-
A
APPENDICES
HIGH-SPEED MACHINE ZERO POINT
RETURN
In this zero point return method the near-point
dog is not detected. The positioning data
address is replaced with the machine zero
point address, and the positioning data is
executed to carry out high-speed positioning to
the zero point at a designated speed.
(This is not validated unless a machine zero
point return has been carried out first.)
Positioning data command speed
Zero point
Near-point dog switch
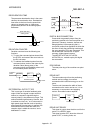
HIGH-SPEED ZERO POINT RETURN
The axis returns to the machine zero point at
the zero point return speed without detecting
the near-point dog.
(This is not validated unless a machine zero
point return has been carried out first.)
Zero point
Near-point dog switch
Zero point return speed
INCREMENT SYSTEM
The current value is 0 in this system. Positions
are expressed by the designated direction and
distance of travel. Also called the relative
address system. This system is used in fixed-
dimension feed, etc. Compare ABSOLUTE
SYSTEM.
No.1 No.2 No.3
0
00
Stop
Left
Right Right
No. 2 is several millimeters
to the right of No. 1.
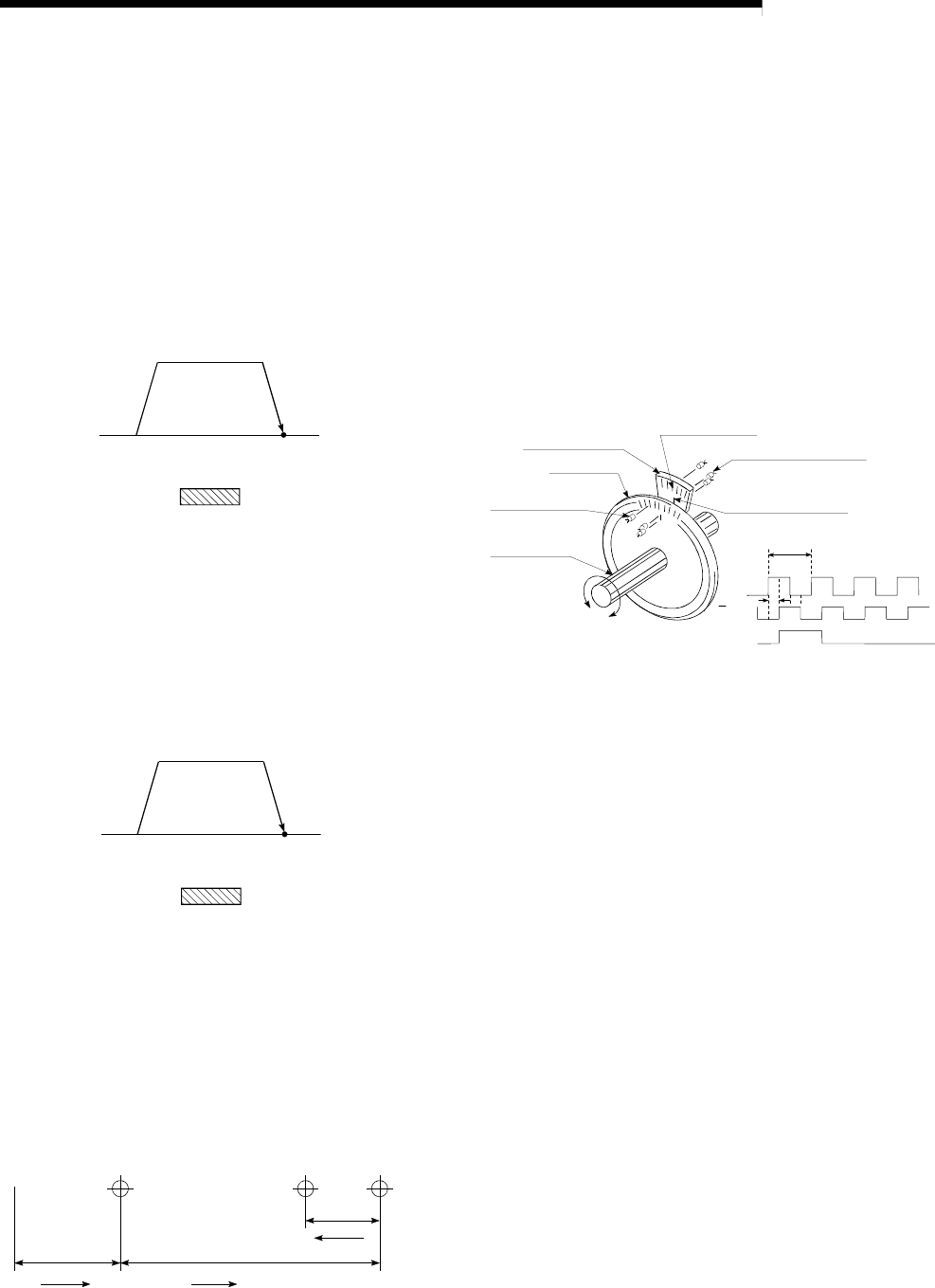
INCREMENTAL ENCODER
A device that simply outputs ON/OFF pulses
by the rotation of the axis. 1-phase types
output only A pulses, and do not indicate the
axis rotation direction. 2-phase types output
both A and B pulse trains, and can judge the
rotation direction. The direction is judged to be
forward if the B pulse train turns ON when A is
ON, and judged to be reverse if A turns ON
when B is ON. There is also another type of
incremental encoder with a zero point signal.
The most commonly used incremental
encoders output between 100 and 10,000
pulses per axis rotation. Refer to "ENCODER".
A
B
A
Z
B
1
4
A signal slit
B signal slit
Slit disk
Light-emitting diode
Phototransistor
Zero signal slit
Rotating axis
1 pitch
pitch
Zero point signal
1 pulse per axis rotation
Output waveform 2-phase + zero point outpu
t
INERTIA
The property of an object, when not being
affected by external forces, where it tries to
maintain its current condition. The inertia
moment.